About the Long Island Rail Road
The Long Island
Railroad is a commuter rail system in the southeastern part of the
U.S. state of New York, stretching from Manhattan to the eastern tip
of Suffolk County on Long Island. With an average weekday ridership of
354,800 passengers in 2016, it is the busiest commuter railroad in
North America. It is also one of the world's few commuter systems that
runs 24 hours a day, seven days a week, year-round. It is publicly
owned by the Metropolitan Transportation Authority, which refers to it
as MTA Long Island Rail Road. Established in 1834 and having operated
continuously since then, it is the oldest railroad in the United
States still operating under its original name and charter. There are
124 stations and more than 700 miles of track on its two lines to the
two forks of the island and eight major branches, with the passenger
railroad system totaling 319 miles of route.
(from
Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia)
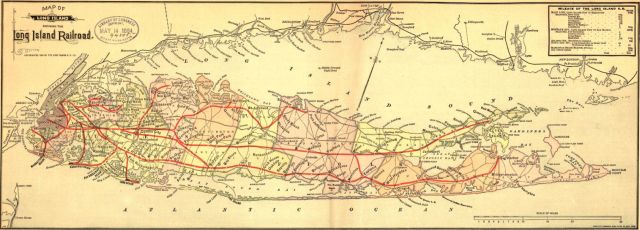
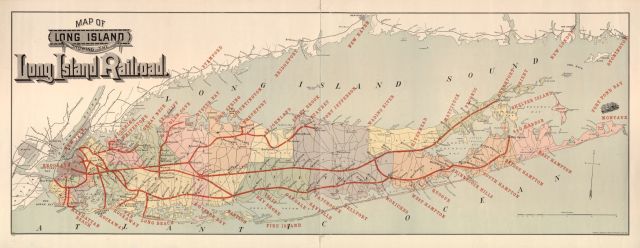
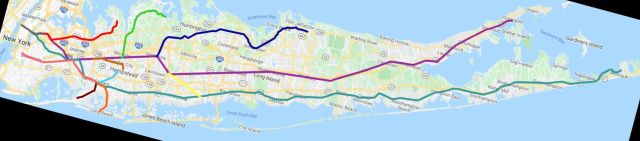
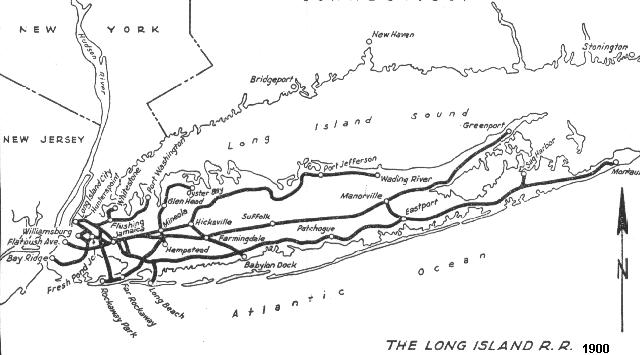
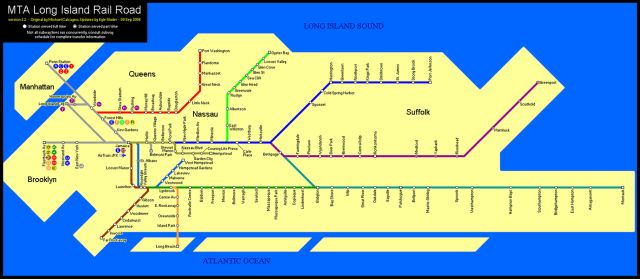
LIRR Maps
Click on any map to see full size
Even more information about the LIRR
Following
are some of the sites that you may wish to visit for various
perspectives on the LIRR.
Wikipedia
Wikipedia, the free
encyclopedia, is a good place to start learning about the LIRR. Its
article includes: History, Major stations, Passenger lines and
services, Fare structure, Accidents and incidents, Train operations,
Equipment, Named trains, and Freight service.
^Top
American Rails
American-Rails.com informs us that
today's LIRR has lost any semblance of independence; as a ward of
the Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA) it provides
commuter rail service between its home island and our nation's
largest city. The "Route Of The Dashing Commuter"
may seem like just another suburban railroad but it carries a rich
history of serving Long Island utilizing an eclectic fleet of
locomotives. The current system provides only passenger service
while freight is now handled by the New York & Atlantic
Railway, a private subsidiary of Anacostia &
Pacific.
^Top
^Top
^Top
^Top
Long Island Rail Road History
The Long Island Rail Road History
Website includes Early History (1834-1900), LIRR Timeline, The
Early Pennsylvania RR Years and Electrification, LIRR Firsts,
Abandoned ROW's and Stations, Individual Branches, System Maps,
Old Timetables, Rolling Stock, Towers, Yards, Trolleys on Long
Island, and 1934 and 1959 100th & 125th Anniversary Booklets.
New York City Subway
The independent New York City subway
site features pages for LIRR lines: Babylon, Far Rockaway,
Flatbush Avenue, Greenport, Hempstead, Long Beach, Long Island
City, Main Line, Montauk, Oyster Bay, Port Jefferson, Port
Washington, Rockaway, and West Hempstead as well as Yards,Photos
With Unknown Locations, and a Route Map.
^Top Trains Are Fun
Trains Are Fun, contains maps of
LIRR freight stations & private sidings in 1966 as well as
numerous links to other information.
Float Bridges of New York Harbor
Transfer Bridges a/k/a Float Bridges
of New York Harbor includes Introduction to Transfer Bridges,
Float Bridge Types, Design Requirements, Float Bridge Appliances,
Carfloat / Float Bridge Interface, Land / Float Bridge Interface
"Bulkhead Anchors", Idler / Reacher Cars, "Bridging" a carfloat
and "Drilling" a carfloat.
Last modified: May 21 2020 13:12:05. Site designed and implemented
by Marshall Abrams